Industrial Ultrafiltration unit is a new type of water treatment and material separation equipment based on membrane separation technology. Driven by pressure difference and using an ultrafiltration membrane with a pore size of 0.001~0.1μm as its core. It achieves efficient separation of molecules of different sizes and solids/liquids through sieving. It can retain impurities such as colloids, bacteria, and viruses, while allowing water molecules and inorganic salts to pass through. With its advantages of high efficiency, energy saving, and ease of operation, it is widely used in water treatment, biomedicine, food, and other industries, and is a key piece of equipment in modern separation technology.

To fully understand the function of an ultrafiltration machine, it is first necessary to clarify its core working mechanism.
How does an industrial ultrafiltration unit work?
Ultrafiltration is a pressure-driven membrane separation process. The entire separation process requires no heating or the addition of any chemical reagents. Only a small amount of external pressure is applied to create a cross-flow state of the feed liquid on the membrane surface.
The ultrafiltration membrane, as the core separation medium, has an asymmetric microporous structure. Its surface layer is a dense microporous layer, primarily responsible for sieving and retaining substances. The bottom layer is a loose support layer, used to ensure the membrane’s mechanical strength. When the feed liquid flows through the membrane surface, substances larger than the membrane pore size (such as colloidal particles, bacteria, viruses, and proteins) are trapped on the feed side of the membrane, forming a concentrate that is periodically discharged. Substances smaller than the membrane pore size (such as water molecules, sodium ions, and chloride ions) can permeate the membrane pores, forming the permeate (i.e., ultrafiltrate). Thus achieving separation, purification, and concentration.
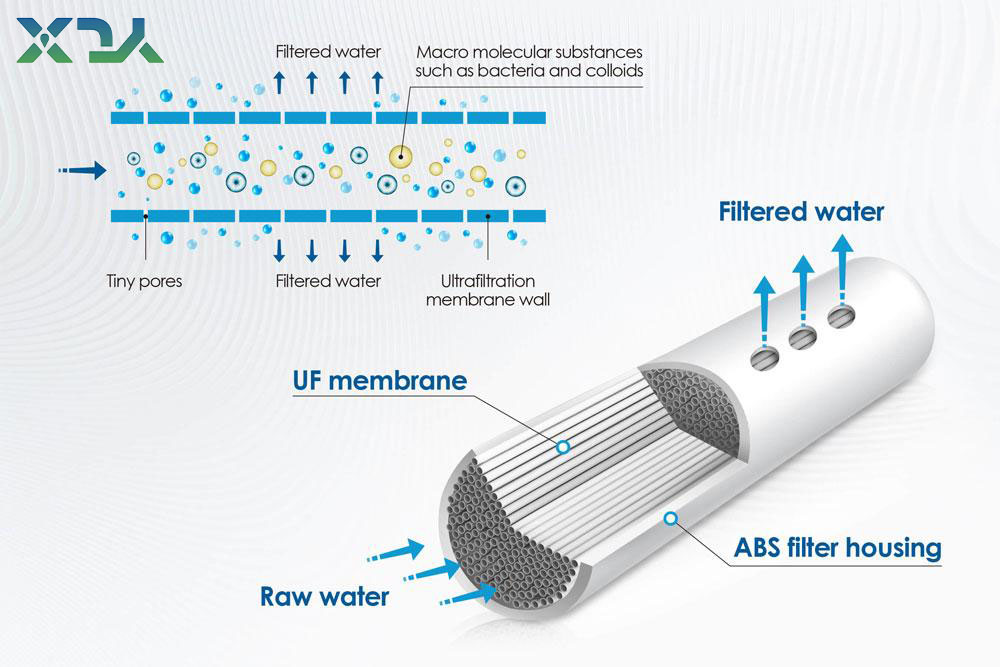
This screening mechanism does not change the chemical properties of the material and can retain the original components of the material to the greatest extent. It is especially suitable for processing heat-sensitive substances. Thus, it is also the core highlight of ultrafiltration system that distinguishes them from traditional filtration, distillation and other separation technologies.
What are the functions of an industrial ultrafiltration unit?
The core functions of industrial ultrafiltration unit can be summarized into three main categories, separation, purification, and concentration. Specifically, this manifests as the precise screening and separation of various substances in different systems. Therefore, it can adapt to the practical application needs of different fields, with each function possessing a clear application scenario and unique technological advantages.
Separation
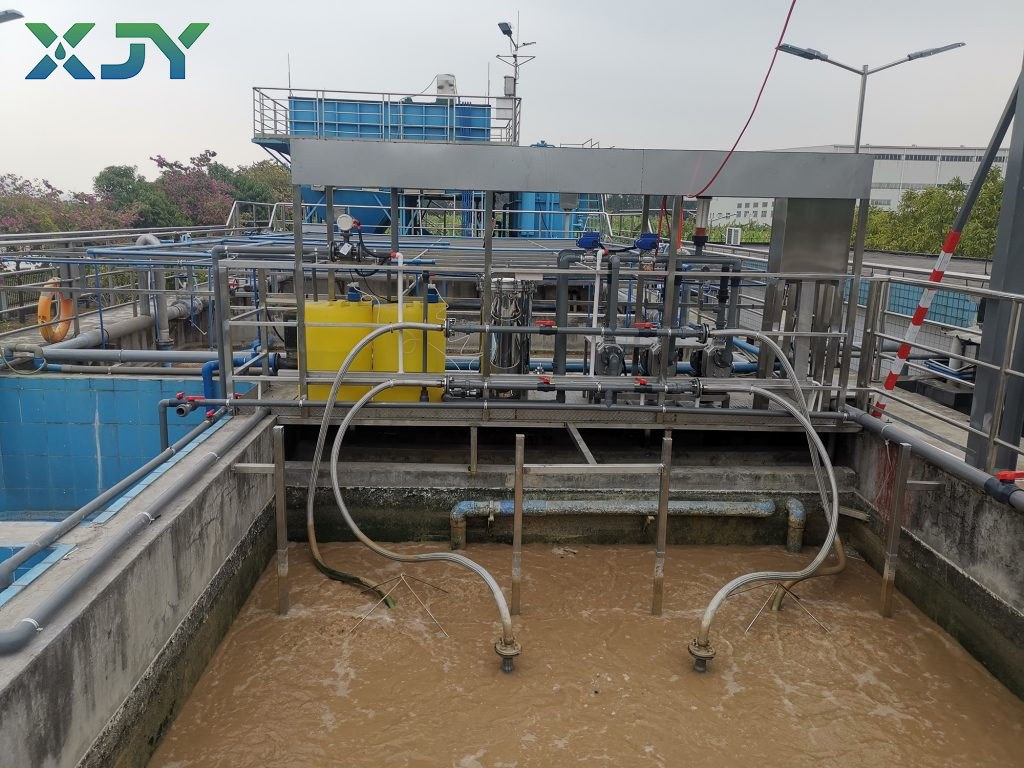
Separation is the most fundamental and widely used function of industrial ultrafiltration unit, primarily for solid-liquid separation. In water treatment, the device efficiently removes suspended solids, colloidal particles, and turbidity from water, while also achieving deep interception of microorganisms. The bacterial removal rate can reach over 99.99%, fundamentally improving water clarity and reducing turbidity and the Solids Indication Dispersion Index (SDI).
Compared to traditional processes such as sand filtration and activated carbon filtration, ultrafiltration unit offer superior separation precision. They are less affected by fluctuations in raw water quality, consistently delivering high-quality water. Even with significant changes in raw water turbidity, the effluent quality remains within acceptable standards. For example, in municipal drinking water treatment, ultrafiltration machine can serve as advanced treatment units, replacing traditional filtration processes to effectively remove trace amounts of colloids and microorganisms that are difficult to remove using conventional methods. In industrial wastewater treatment, it can remove colloidal impurities and suspended pollutants, providing pretreatment for subsequent reverse osmosis treatment, preventing colloidal contamination of the reverse osmosis membrane, extending its lifespan, and reducing overall water treatment costs.

Purification
Purification is one of the core applications of industrial ultrafiltration unit in fine chemicals, biomedicine, and food and beverage industries. Its core purpose is to remove impurities from materials while retaining the target active ingredients, achieving purification and refinement.
In the food and beverage industry, the purification function of ultrafiltration system is widely used. For example, in the production of fruit juice, the juice contains a large amount of impurities such as pectin, protein, and suspended particles, which affect the juice’s clarity, stability, and taste. Ultrafiltration machine can remove large molecular impurities such as pectin and protein through sieving, while retaining the effective components such as sugars, vitamins, and minerals, resulting in a clear and stable fruit juice product. Simultaneously, no clarifying agents or other chemical substances are needed, ensuring the natural quality of the juice.
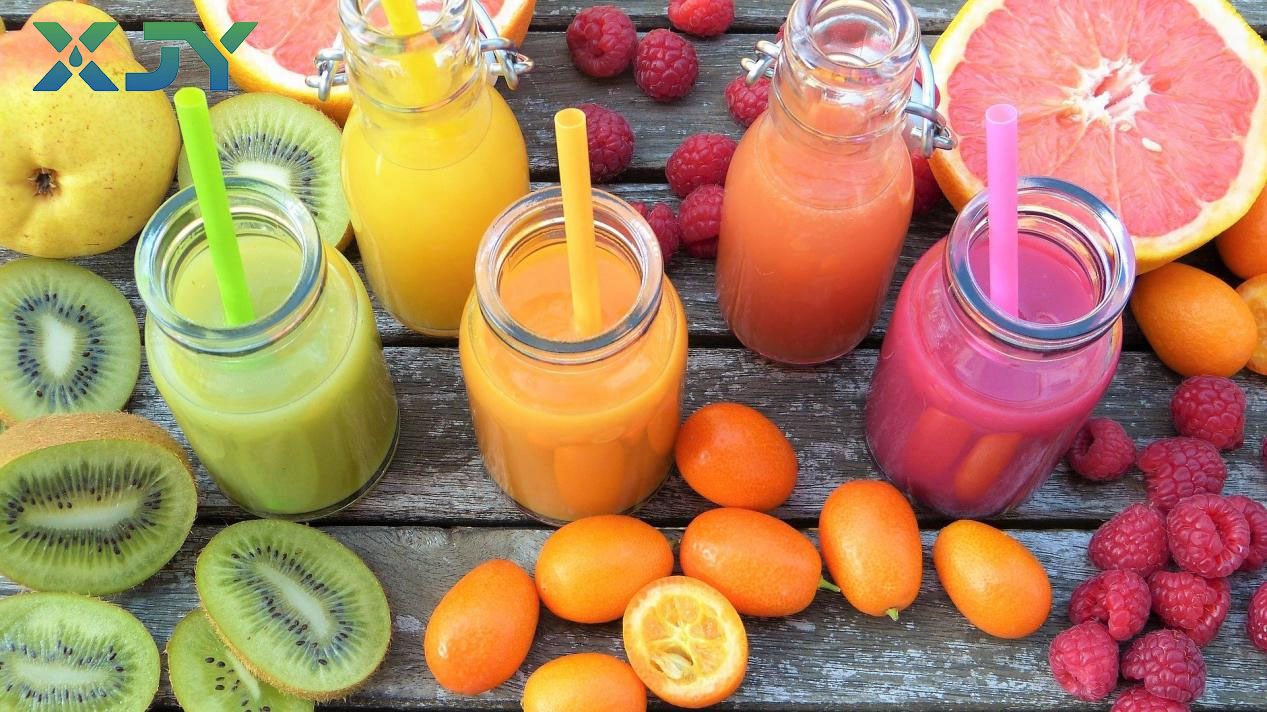

In dairy production, ultrafiltration systems can be used to purify whey protein, removing small molecule impurities such as lactose and inorganic salts to obtain high-purity whey protein. This can be used to produce high-end products such as whey protein powder and infant formula, increasing the added value of dairy products.
Concentration
Concentration is another important function of industrial ultrafiltration unit. It is mainly used to concentrate target substances in dilute solutions, reducing solution volume and increasing the concentration of the target substance, facilitating subsequent storage, transportation, and processing. It also enables resource recovery and reuse. The core advantages of concentration are low energy consumption and gentle operation. And it eliminates the need for heating and evaporation, avoiding denaturation and decomposition of the target substance due to high temperatures, making it particularly suitable for processing heat-sensitive substances.
In the food and beverage industry, concentration is widely used. For example, in the production of fruit and vegetable juices, ultrafiltration machine can concentrate diluted juices, increasing the juice concentration, reducing transportation and storage costs, while preserving the juice’s nutrients and original flavor.
In dairy production, whey protein solutions can be concentrated to achieve the required whey protein concentration for the production of high-end dairy products, achieving efficient utilization of whey resources and reducing waste.
Other functions
Besides its core functions of separation, purification, and concentration, industrial ultrafiltration unit also provide auxiliary functions such as pretreatment, purification, and recovery. In the field of water treatment, ultrafiltration system is often used as pretreatment units in advanced treatment processes such as reverse osmosis and nanofiltration. By removing impurities such as colloids, suspended particles, and microorganisms from the water, they reduce the water’s Solids Index (SDI). For example, in seawater desalination and ultrapure water production, ultrafiltration pretreatment is an essential step, effectively removing impurities such as colloids, algae, and microorganisms from seawater, protecting the reverse osmosis membrane. And improve the efficiency and stability of seawater desalination and ultrapure water production.
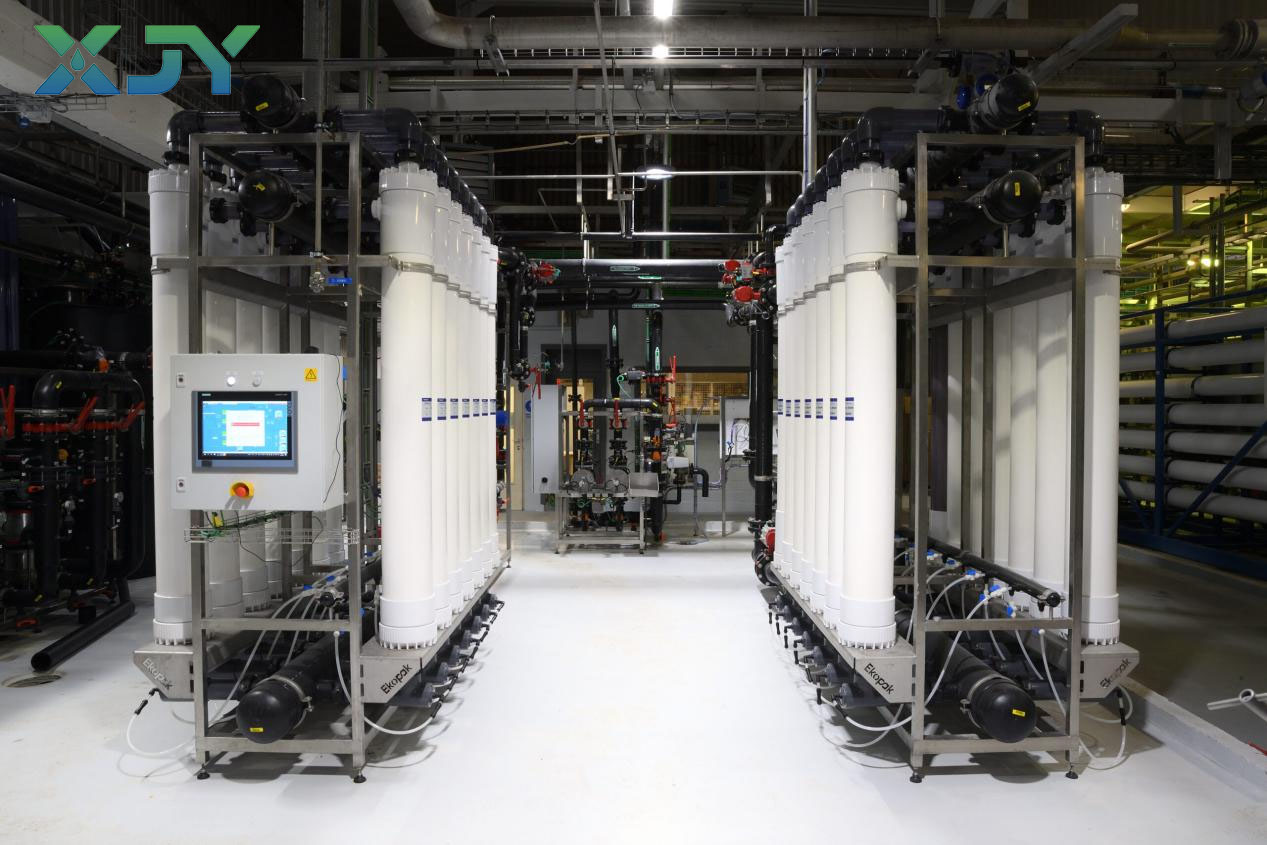

With the continuous advancement of membrane technology, the performance of ultrafiltration machine is constantly improving, and their application range is continuously expanding. The research and application of novel ultrafiltration membrane materials (such as modified polysulfone membranes and ceramic membranes) have further improved the separation accuracy, fouling resistance, and service life of ultrafiltration devices. The combined use of ultrafiltration system with other separation technologies (such as reverse osmosis, nanofiltration, and ion exchange) achieves complementary advantages and expands its application in high-end fields, such as ultrapure water preparation, biopharmaceutical purification, and high-end food processing.
Resumir
Today, industrial ultrafiltration unit is widely used in various fields such as municipal water treatment, industrial wastewater treatment, biomedicine, food and beverage, chemical industry, electronics, and environmental protection. They play an irreplaceable and important role in ensuring drinking water safety, controlling environmental pollution, improving resource utilization, and promoting industrial upgrading.











