Desalination machine works by using pressure to overcome osmotic pressure, separating water from salt through a special semipermeable membrane.
Compared to traditional distillation, they do not require extensive heat energy and consume only one-third to one-half the energy of distillation. A single unit can produce from a few tons to hundreds of thousands of tons of fresh water per day, meeting both daily water and large industrial needs.

What is the operating process of a seawater desalination machine?
1. Pretreatment: Clearing the way for reverse osmosis membrane components
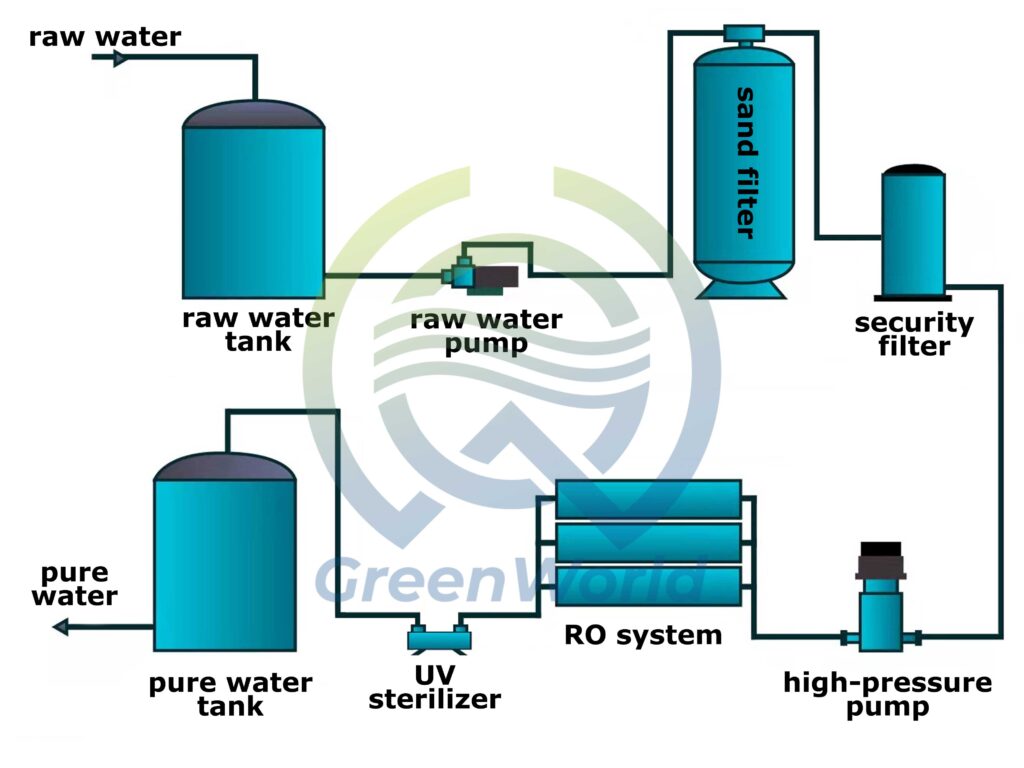
Before entering the reverse osmosis membrane, seawater must undergo rigorous pretreatment. This step is crucial for ensuring the long-term stable operation of the equipment. First, after entering the equipment, the seawater enters a multi-media filter filled with quartz sand, activated carbon, and other filter media. This filter removes suspended matter, silt, algae, and other impurities larger than 5 microns in diameter, preventing subsequent pipe blockage.
The seawater then flows into a precision filter, where the pore size is reduced to 1-5 microns, further trapping tiny colloidal particles and residual suspended matter. Simultaneously, the system automatically adds antiscaling agents to the water to prevent the formation of scale on the membrane surface caused by calcium and magnesium ions in the subsequent high-pressure environment.
After pretreatment, the seawater’s turbidity drops to below 0.1 NTU, meeting the standard for entering the reverse osmosis membrane module.
2. High-pressure separation: reverse osmosis membrane molecular screening
The pretreated seawater is then pumped to a high-pressure pump, which increases the pressure to force water molecules through the membrane. The pressurized seawater then enters the reverse osmosis membrane module.
The pore size of the reverse osmosis membrane is only 0.1 nanometer, smaller than the diameter of a sodium chloride molecule in seawater (approximately 0.5 nanometers). Under high pressure, the RO membrane allows water molecules to pass through and form fresh water, while retaining impurities such as salt ions, heavy metal ions, and organic matter to form concentrated brine. The membrane’s retention rate exceeds 97%, effectively removing salt and contaminants from seawater.
3. Post-processing: Make fresh water reach customized standards
Although the system has largely desalinated the freshwater, it still needs to adjust the freshwater’s pH to meet usage requirements. First, the freshwater enters a pH adjustment system, where chemicals such as sodium hydroxide are added to adjust the pH from 5.5-6.5 to 7.0-8.5, preventing acidic water from corroding pipes.
For domestic drinking water, the freshwater also passes through a mineral addition system. Calcium, magnesium, and other minerals are added to enhance its taste.
lue. Ultraviolet disinfection also eliminates any remaining bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms in the water, ensuring safe drinking water.
Finally, we can transport the treated freshwater to storage tanks and then distribute it to consumers through the pipeline network.
4. Maintenance: Maintenance equipment
After long-term operation, contaminants such as colloids, microorganisms, and scale may adhere to the surface of reverse osmosis membranes. These contaminants can reduce the membrane’s permeability and retention rate. Therefore, the membrane cleaning system regularly cleans the membrane assembly through acid cleaning (to remove scale) and alkaline cleaning (to remove organic matter and microorganisms). This can restore membrane performance. And extend its service life (typically, reverse osmosis membranes have a service life of 3-5 years).
Why use a reverse osmosis desalination machine?
Compared with other desalination technologies, the use of seawater reverse osmosis technology has unique advantages.
- First, it has low energy consumption, no need for heating, and lower operating costs.
- Secondly, it occupies a small area and has a compact equipment structure. Thus, the structure is suitable for coastal areas or islands with limited space.
- Third, it is highly flexible and can adjust the scale of equipment according to water demand, from small mobile equipment to large seawater desalination plants.
- Fourth, the water quality is good. The salinity of desalinated fresh water can be reduced to below 500 mg/L (the standard for drinking water is below 1000 mg/L), meeting various water needs.
Summarize
In short, desalination system is to use a high-pressure pump to pressurize seawater to a level exceeding its osmotic pressure. It allows water molecules to penetrate a RO membrane with pores as small as 0.1 nanometers and become fresh water. The membrane traps impurities such as salt ions and heavy metal ions, forming a concentrated brine. Thus it can achieve water-salt separation.
If you require information about this type of water treatment equipment, please feel free to contact us.