According to UN data, over one-third of the world’s population faces water scarcity. Therefore, the global shortage of freshwater resources severely impacts human societal development. Against this backdrop, the urgent need for freshwater among residents in arid and water-scarce coastal areas has driven the rapid development of seawater desalination technology. Through ro desalination system, bitter seawater can be transformed into usable freshwater.
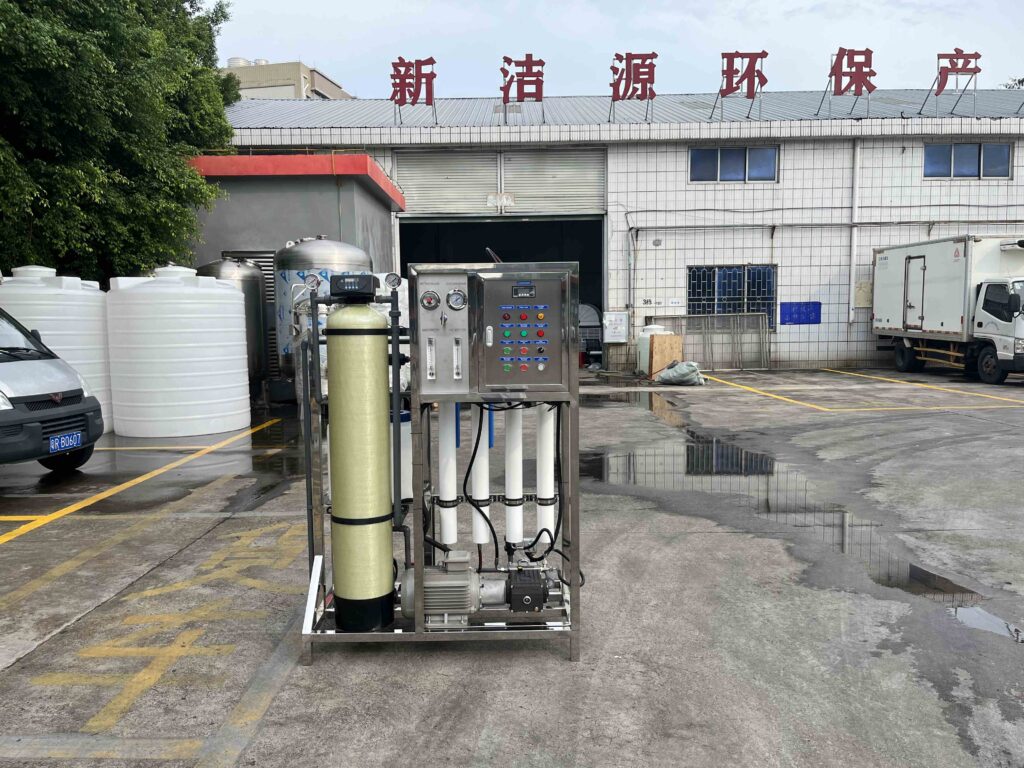

What is the components of a ro desalination system?
A fully functional ro desalination system mainly consists of three key parts: pretreatment, the reverse osmosis unit, and post-treatment. Each stage plays an irreplaceable role.
① The pretreatment stage utilizes mature technologies such as quartz sand filtration and activated carbon adsorption to remove silt particles, colloidal substances, and organic pollutants from seawater, preventing fouling or clogging of the subsequent membrane modules.
② The reverse osmosis unit is the “core power zone” of the system. High-pressure pumps increase the seawater pressure to 6 to 8 MPa, providing the necessary power for the reverse osmosis process. The membrane modules separate water molecules from impurities.
③ The post-treatment stage optimizes the taste of the water by adjusting the pH value and supplementing appropriate minerals, ensuring that the final effluent meets drinking water standards.

Compared to distillation, what is the differences between ro desalination system?
First, reverse osmosis and traditional distillation differ significantly in their core driving forces and processing procedures for seawater desalination.
RO desalination system: Powered by pressure (pressurized to 6-8 MPa by a high-pressure pump), it utilizes a semi-permeable membrane with a pore size of 0.1 nm to trap salt ions and contaminants, allowing only water molecules to pass through, thus achieving separation. Process: Pretreatment (quartz sand/activated carbon impurity removal) → High-pressure pump pressurization → Membrane module separation (water molecule penetration, impurity trapping) → Post-treatment (pH adjustment/mineral replenishment).
Distillation: Powered by heat, it heats seawater to its boiling point, vaporizing it, and utilizes the difference in boiling points between water and salts to achieve separation. Process: Seawater preheating → Heating to boiling point → Steam condensation into liquid freshwater → Collection.
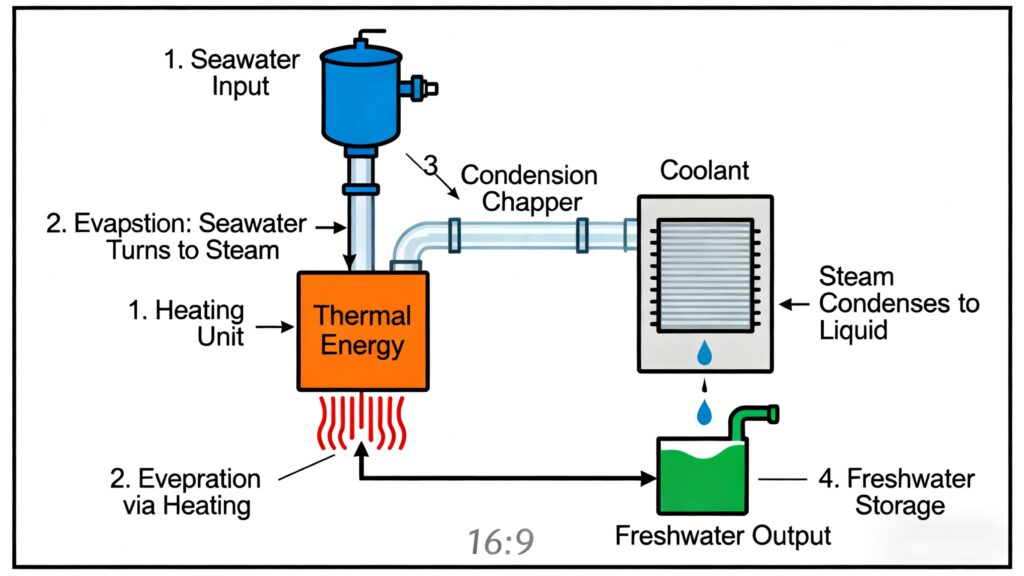
Secondly, compared to traditional distillation-based seawater desalination technology, reverse osmosis technology offers significant energy savings.
Distillation requires heating seawater to a boiling point, resulting in extremely high energy costs. Reverse osmosis, on the other hand, uses only pressure to drive the separation process, consuming less than a quarter of the energy of distillation.
Reverse osmosis membranes not only possess stronger anti-fouling properties but also have a lifespan extended from 2-3 years in the past to over 5 years, significantly reducing system maintenance costs.
Currently, the world’s largest ro desalination plant—the Jubail Desalination Plant in Saudi Arabia—can produce 1.4 million cubic meters of fresh water daily, providing a solid guarantee for the production and domestic water needs of millions of people.
What is the shortcomings of ro desalination system?
Despite its significant advantages, ro desalination system still faces several pressing challenges.
For example, the direct discharge of high-salinity concentrate generated during desalination could adversely affect the nearshore marine ecosystem. Currently, the industry has mitigated this problem to some extent through methods such as concentrate dilution and discharge, and recycling in conjunction with the salt chemical industry.
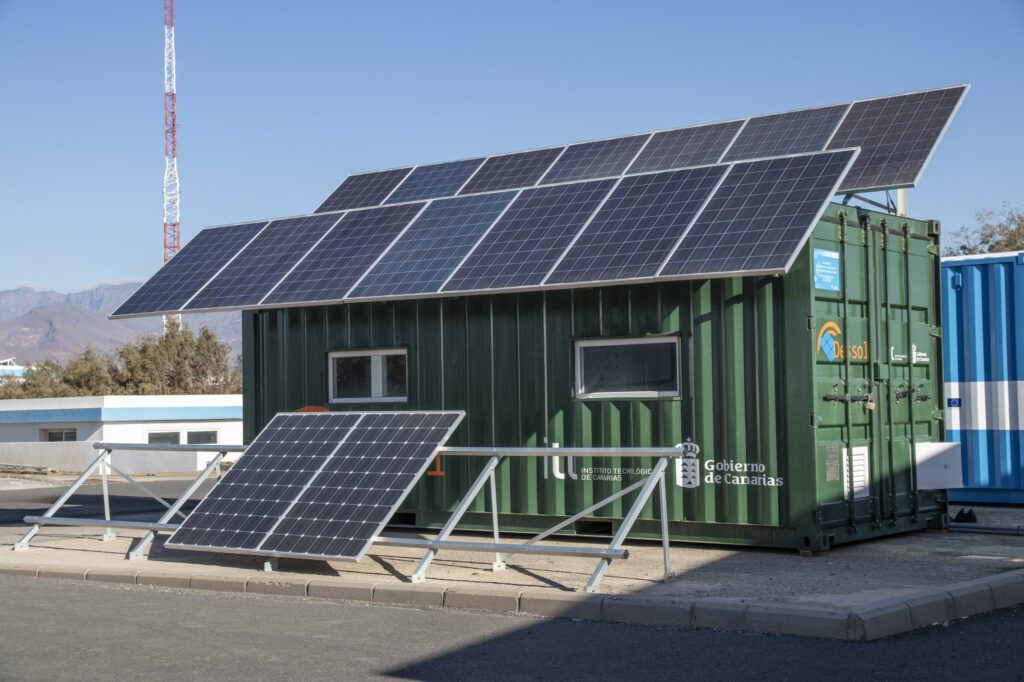
Furthermore, in regions where fossil fuels are the primary source of electricity, the system’s operation indirectly generates carbon emissions. Therefore, domestic and international research institutions are actively promoting the integration of photovoltaics and seawater desalination, utilizing clean solar energy to power the system and achieving green synergy between water resource development and energy utilization.
Summarize
RO desalination System has been widely used in many countries, including the United States, Canada, and Peru, both domestically and internationally. With the continuous innovation of membrane material technology, this system will not only play a greater role in water supply security, but will also provide stable and reliable freshwater supply services for special scenarios such as remote islands and ocean-going vessels, relying on containerized mobile equipment.












