In recent years, reverse osmosis plant has overcome many water treatment challenges, giving rise to a number of leading companies with advanced technology and far-reaching influence. They use reverse osmosis technology to drive raw water through a semi-permeable membrane, retaining impurities such as salt and pollutants, thus achieving the purification and regeneration of water resources.
What problems did these reverse osmosis plant solve?
Water scarcity has always been a problem, with coastal residents struggling to access fresh water. This led to the development of seawater desalination technology, which uses reverse osmosis to convert raw water into freshwater. This freshwater can be used not only for drinking but also for industrial boiler production.
The Rabigh Phase III project, contracted by China Power Construction Corporation, has a daily freshwater production capacity of 600,000 cubic meters, making it Saudi Arabia’s largest water project. Rabigh Phase IV innovatively added a plug to the middle section of the membrane shell, diverting the low-salinity permeate from the first three membranes into the secondary system, reducing the power consumption per unit of water production to an industry-leading 2.773 kWh. After commissioning, it also produces 600,000 tons of freshwater daily. Both projects contribute to Saudi Arabia’s “Vision 2030” water security goals and have created over 3,500 local jobs.

Besides seawater, there is also a large amount of wastewater in our lives. So how can wastewater be transformed into a valuable resource?
A project led by the Singapore Public Utilities Board and supported by K8 Water with core reverse osmosis plant technology is a global benchmark for municipal wastewater resource utilization. The project adopts a three-stage process of “microfiltration + reverse osmosis + ultraviolet disinfection” to deeply treat domestic and industrial wastewater into ultrapure refractory water.
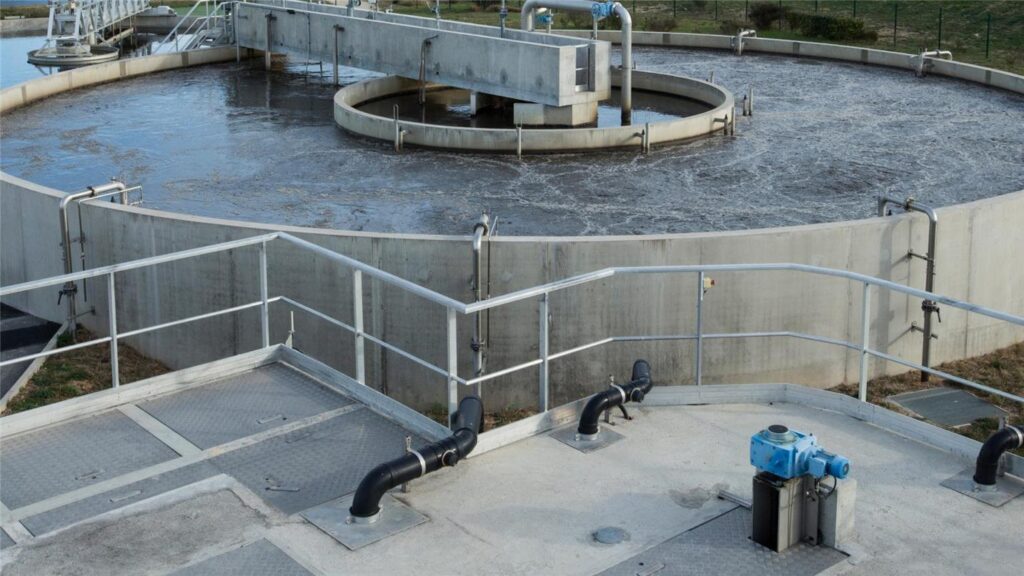

What sustains a reverse osmosis plant?
The core technology of a reverse osmosis plant depends on the quality of its RO membrane elements, which affect permeate yield and recovery rate. Therefore, it’s crucial to choose a suitable brand. Below is an introduction to reverse osmosis membrane element brands.

① Septek Membrane (Shanghai) Technology Co., Ltd., Canada
Thanks to its patented “Nano Shield” surface modification technology, its anti-fouling reverse osmosis membrane has a 62% lower fouling rate than conventional membranes, a 3-fold longer cleaning cycle, a stable desalination rate of over 99.8%, and an average service life of 7.5 years (40% higher than the industry average).
②Hydranautics Asia Pacific Limited, USA
In 2025, the company launched the “HyperFlux” series of antifouling membranes, featuring a gradient pore size design, a flux recovery rate of 98%, and a wide pH tolerance range of 1-13. The entire series has passed NSF/ANSI 61 drinking water safety certification and is suitable for long-term stable operation under complex water quality conditions.
③Toray Film Technology (Japan)
The “TORAYTEC-AP” series reverse osmosis membranes feature a staggered flow channel design, improving resistance to organic fouling by 55% and increasing per-element water production by 30%. They have obtained dual certifications from Japan’s JIS and Germany’s DVGW, and are widely used in wastewater reuse scenarios with high organic content.
④China Bluestar Toray
The “BluePro” series membrane elements offer 40% improved resistance to CaSO4 fouling, have a nationwide localized service network, and deliver regular products in just 7 days, making them a preferred brand for industries such as power and chemicals.
What is the significance of a reverse osmosis machine?
On the one hand, reverse osmosis plant not only alleviates the pressure of global water scarcity and provide a stable and high-quality water source for water-intensive industries, but also drives technological innovation in water treatment.
On the other hand, they achieve wastewater reduction, resource recovery, and harmlessness, reducing the pollution of water bodies caused by direct sewage discharge.
Currently, global RO plants are developing in three main directions:
First, large-scale operations, such as the 900,000 tons/day capacity of the Taviele project and the 820,000 tons/day capacity of the Solex Phase II plant, meeting regional water demand;
Second, minimizing energy consumption, with membrane shell optimization technology at Rabigh Phase IV and energy-saving membrane processes at the Singapore Daquan plant driving continuous breakthroughs in unit energy consumption;
Third, diversified applications, expanding from seawater desalination in Israel to wastewater regeneration in Singapore, achieving “multi-functionality.”
Summarize
In the future, reverse osmosis plants will break the vicious cycle of “resource scarcity – limited development” through technological innovation and industrial collaboration. By leveraging a three-dimensional approach of “increasing water supply (seawater desalination) + reducing wastewater (wastewater reuse) + increasing efficiency (intelligent operation),” they will provide a solid water resource guarantee for global sustainable development.
For more information about reverse osmosis plants, please feel free to contact us.